深浅模式
MSBlock(💯)
一、本文介绍
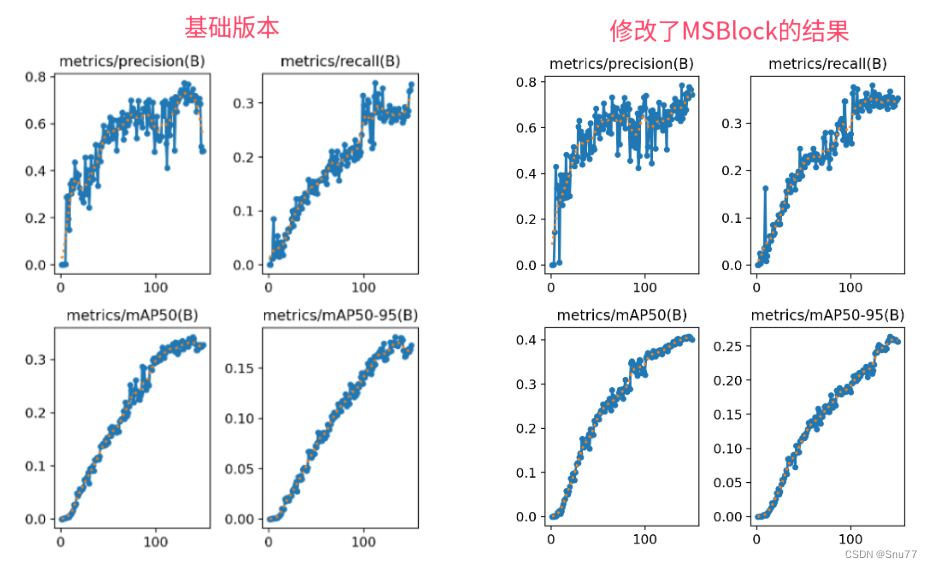
本文给大家带来的改进机制是利用YOLO-MS提出的一种针对于实时目标检测的MSBlock模块(其实不能算是Conv但是其应该是一整个模块),我们将其用于C2f中组合出一种新的结构,来替换我们网络中的模块可以达到一种轻量化的作用,我将其用于我的数据集上实验,包括多个类别的数据集,其在轻量网络结构的同时,却能够提高一定的mAP精度,所以这是一种十分高效的模块,该网络结构非常适合那些模型精度已经无法提到,想要从轻量化模型的角度入手的读者使用,同时该机制包含二次创新的机会。

二、MSBlock
 论文地址:论文官方地址
论文地址:论文官方地址
代码地址:官方代码地址

2.1 MSBlock的基本原理
MSBlock的基本原理在于提高实时目标检测器的多尺度特征表示能力。MSBlock通过采用层次化特征融合策略和异构卷积核选择协议,有效地在网络不同阶段处理不同尺度的特征。这种设计使得检测器能够更好地识别和处理不同尺寸的目标。MSBlock的核心思想是通过改进卷积核的大小和结构,以及优化特征融合方式,来增强模型在处理多尺度信息时的性能,从而提高整体的目标检测精度和效率。
MSBlock的基本原理可以分为以下几点:
1. 多尺度特征表示:MSBlock旨在增强实时目标检测器处理不同尺度目标的能力,通过有效地表示和融合不同尺度的特征。
2. 层次化特征融合:MSBlock采用层次化的方式来融合来自网络不同层次的特征,这有助于模型在处理细粒度和粗粒度信息时的表现。
3. 异构卷积核选择:MSBlock实施一种异构卷积核选择协议,即在网络的不同阶段使用不同大小的卷积核,以适应不同尺度的特征表示。
下面我们可以看到三种不同的网络构建模块,分别是CSP Block、ELAN Block和MS-Block。
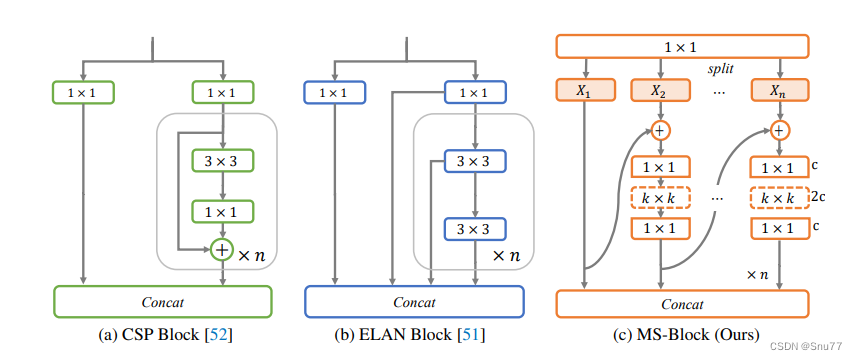
MS-Block设计包含以下特点:
1. 输入被分割成多个分支,每个分支处理不同的特征子集。
2. 在分支内部,通过1x1卷积进行特征转换,然后应用了一个kxk的深度卷积(深度可分离卷积),再接一个1x1卷积,以增强特征并减少参数数量。
3. 最后,所有的分支再经过一个1x1卷积进行融合,以整合各个分支的特征。
2.2 多尺度特征表示
在本文中,多尺度特征表示是通过MSBlock实现的,它通过在网络的不同层使用不同大小的卷积核来捕捉不同尺度的图像特征。这使得模型能够在低层捕获细节和小尺寸目标的特征,同时在高层捕捉更大区域的特征,有助于识别大尺寸目标。
2.3 层次化特征融合
层次化特征融合是通过MSBlock实现的,该技术利用多个并行处理的子网络或分支来处理输入特征图。这些分支在处理不同尺度的特征后,再通过特定的结构(如1x1卷积)融合这些特征,这样的结构设计允许网络在多个层次上提取和整合特征,提高了对各种尺寸目标的检测性能。
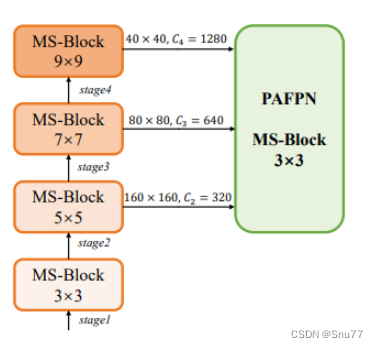
在这张图片中,我们看到了HKS(异构Kernel选择)协议的示意图,这个协议是在YOLO-MS中提出来的。HKS协议通过在网络的不同阶段使用不同大小的卷积核,来优化多尺度特征的提取。在这个图中,从上到下,MS-Block在网络的四个阶段分别使用了9x9、7x7、5x5和3x3的卷积核大小,这种设计允许网络更有效地处理不同尺度的对象,而且每个阶段的输出特征图大小和通道数(C1, C2, C3, C4)也有所不同。最终,通过PAFPN模块将这些特征进一步融合,以增强网络对多尺度特征的捕获能力。
2.4 异构卷积核选择
异构卷积核选择是指在深度学习模型中,根据数据的不同层次和尺度选择不同大小的卷积核。在论文中,通过这种方式,网络可以根据特征图的分辨率调整卷积核的大小,使得在捕捉小目标特征时使用较小的卷积核,在捕捉大目标特征时使用较大的卷积核。这样的设计有助于模型更精细地捕捉不同尺度的图像特征,并提高了目标检测的准确性和效率。
三、MSBlock的核心代码
使用方式看章节四
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
__all__ = ['C2f_MSBlock']
def autopad(k, p=None, d=1): # kernel, padding, dilation
"""Pad to 'same' shape outputs."""
if d > 1:
k = d * (k - 1) + 1 if isinstance(k, int) else [d * (x - 1) + 1 for x in k] # actual kernel-size
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
class Conv(nn.Module):
"""Standard convolution with args(ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups, dilation, activation)."""
default_act = nn.SiLU() # default activation
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, d=1, act=True):
"""Initialize Conv layer with given arguments including activation."""
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p, d), groups=g, dilation=d, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
"""Apply convolution, batch normalization and activation to input tensor."""
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
"""Perform transposed convolution of 2D data."""
return self.act(self.conv(x))
class MSBlockLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inc, ouc, k) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.in_conv = Conv(inc, ouc, 1)
self.mid_conv = Conv(ouc, ouc, k, g=ouc)
self.out_conv = Conv(ouc, inc, 1)
def forward(self, x):
return self.out_conv(self.mid_conv(self.in_conv(x)))
class MSBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inc, ouc, kernel_sizes, in_expand_ratio=3., mid_expand_ratio=2., layers_num=3,
in_down_ratio=2.) -> None:
super().__init__()
in_channel = int(inc * in_expand_ratio // in_down_ratio)
self.mid_channel = in_channel // len(kernel_sizes)
groups = int(self.mid_channel * mid_expand_ratio)
self.in_conv = Conv(inc, in_channel)
self.mid_convs = []
for kernel_size in kernel_sizes:
if kernel_size == 1:
self.mid_convs.append(nn.Identity())
continue
mid_convs = [MSBlockLayer(self.mid_channel, groups, k=kernel_size) for _ in range(int(layers_num))]
self.mid_convs.append(nn.Sequential(*mid_convs))
self.mid_convs = nn.ModuleList(self.mid_convs)
self.out_conv = Conv(in_channel, ouc, 1)
self.attention = None
def forward(self, x):
out = self.in_conv(x)
channels = []
for i, mid_conv in enumerate(self.mid_convs):
channel = out[:, i * self.mid_channel:(i + 1) * self.mid_channel, ...]
if i >= 1:
channel = channel + channels[i - 1]
channel = mid_conv(channel)
channels.append(channel)
out = torch.cat(channels, dim=1)
out = self.out_conv(out)
if self.attention is not None:
out = self.attention(out)
return out
class C2f_MSBlock(nn.Module):
"""Faster Implementation of CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
"""Initialize CSP bottleneck layer with two convolutions with arguments ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups,
expansion.
"""
super().__init__()
self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(MSBlock(self.c, self.c, kernel_sizes=[1, 3, 3]) for _ in range(n))
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward pass through C2f layer."""
y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1))
y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
def forward_split(self, x):
"""Forward pass using split() instead of chunk()."""
y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))
y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))四、MSBlock的添加方式
4.1 修改一
第一还是建立文件,我们找到如下ultralytics/nn文件夹下建立一个目录名字呢就是'Addmodules'文件夹,然后在其内部建立一个新的py文件将核心代码复制粘贴进去即可。
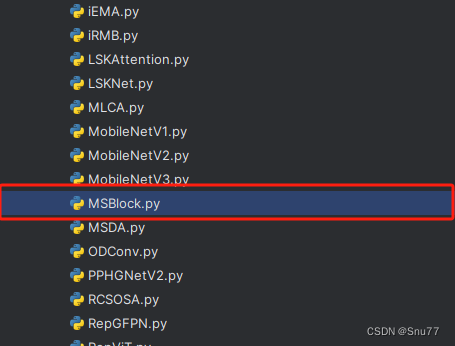
4.2 修改二
第二步我们在该目录下创建一个新的py文件名字为'__init__.py',然后在其内部导入我们的检测头如下图所示。
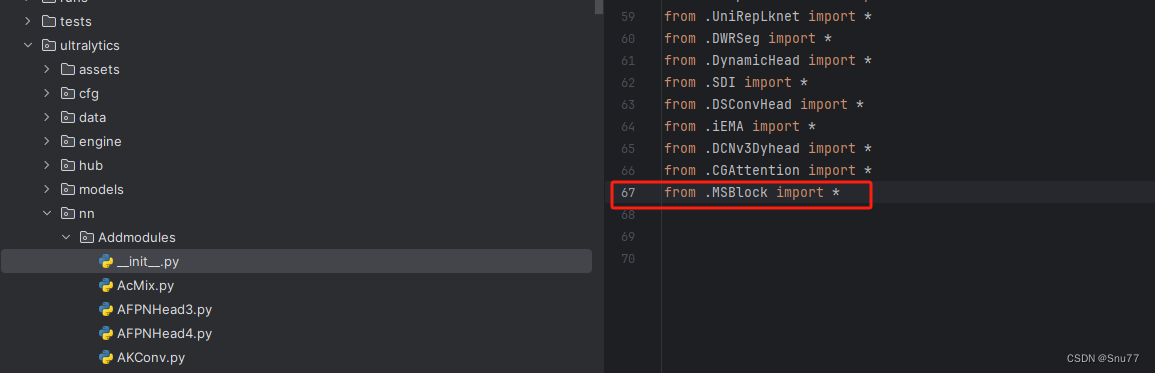
4.3 修改三
第三步我门中到如下文件'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'进行导入和注册我们的模块。
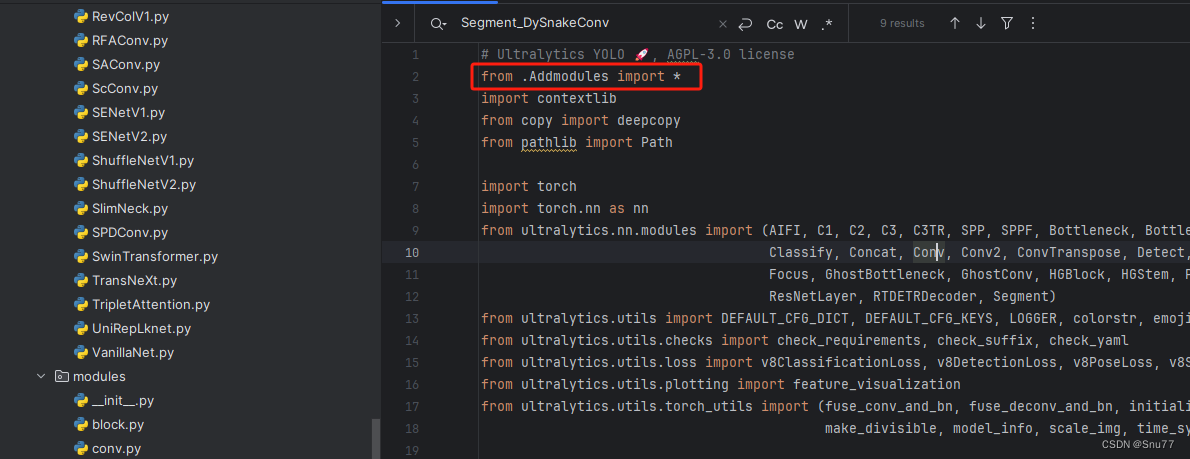
4.4 修改四
按照我的添加在parse_model里添加即可。
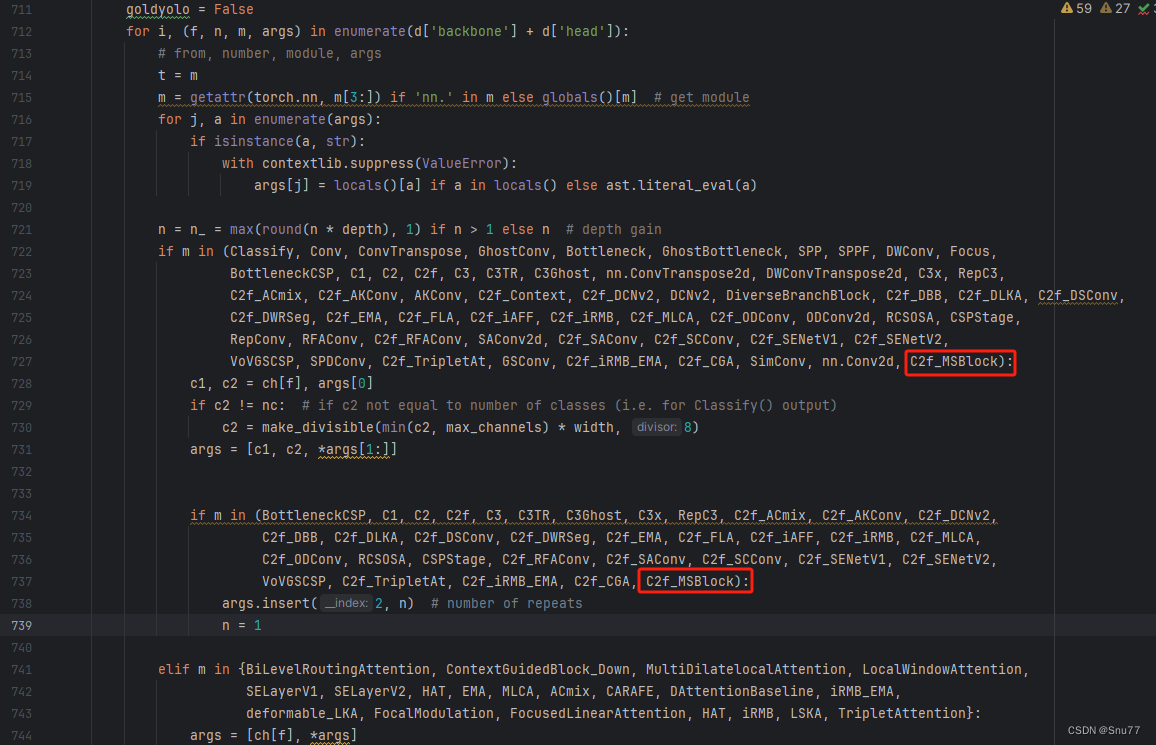
到此就修改完成了,大家可以复制下面的yaml文件运行。
五、MSBlock的yaml文件和运行记录
5.1 MSBlock的yaml文件一
下面的添加MSBlock是我实验结果的版本。
python
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f_MSBlock, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f_MSBlock, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)5.2 MSBlock的yaml文件二
python
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)5.3 MSBlock的yaml文件三
python
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f_MSBlock, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
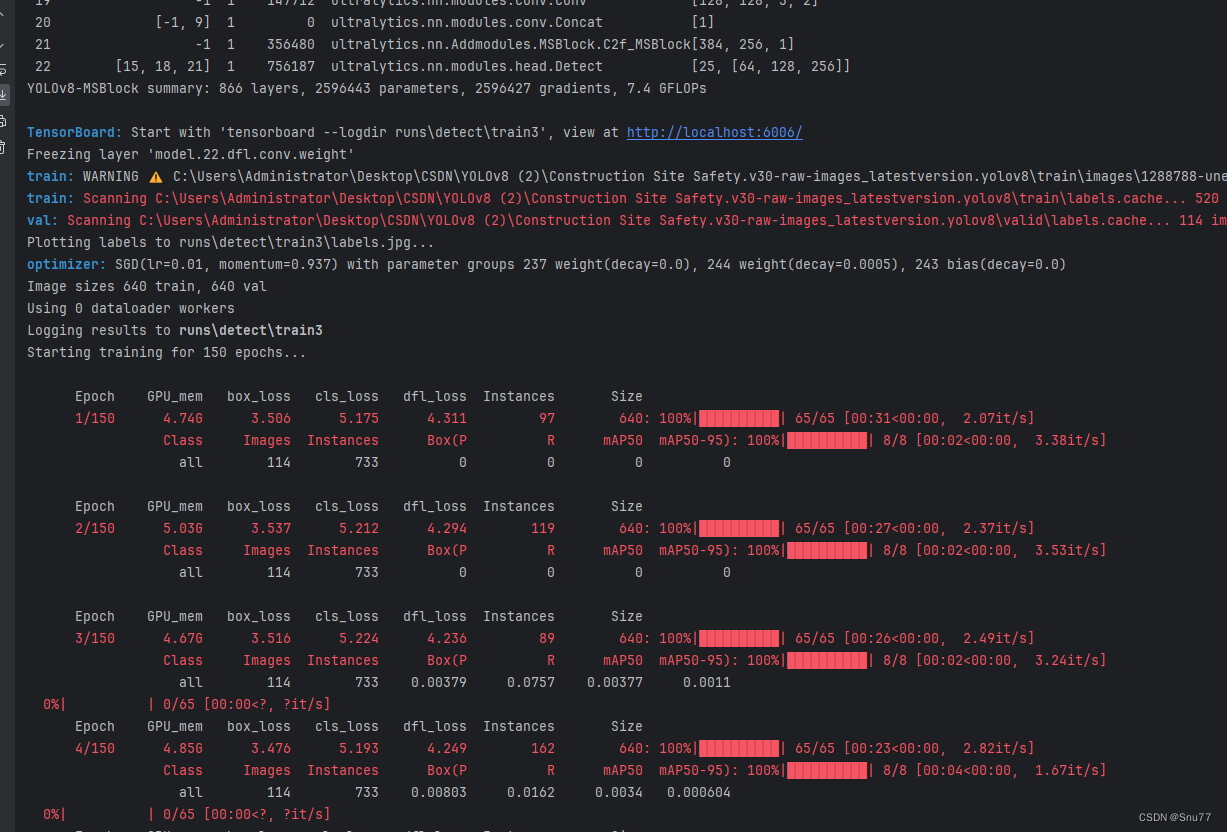
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)5.4 MSBlock的训练过程截图