深浅模式
多尺度空洞注意力 (💯)
一、本文介绍
本文给大家带来的改进机制是MSDA(多尺度空洞注意力)发表于今年的中科院一区(算是国内计算机领域的最高期刊了),其全称是"DilateFormer: Multi-Scale Dilated Transformer for Visual Recognition"。MSDA的主要思想是通过线性投影得到特征图X的相应查询、键和值。然后,将特征图的通道分成n个不同的头部,并在不同的头部中以不同的扩张率执行多尺度SWDA来提高模型的处理效率和检测精度。亲测在小目标检测和大尺度目标检测的数据集上都有大幅度的涨点效果(mAP直接涨了大概有0.06左右)。
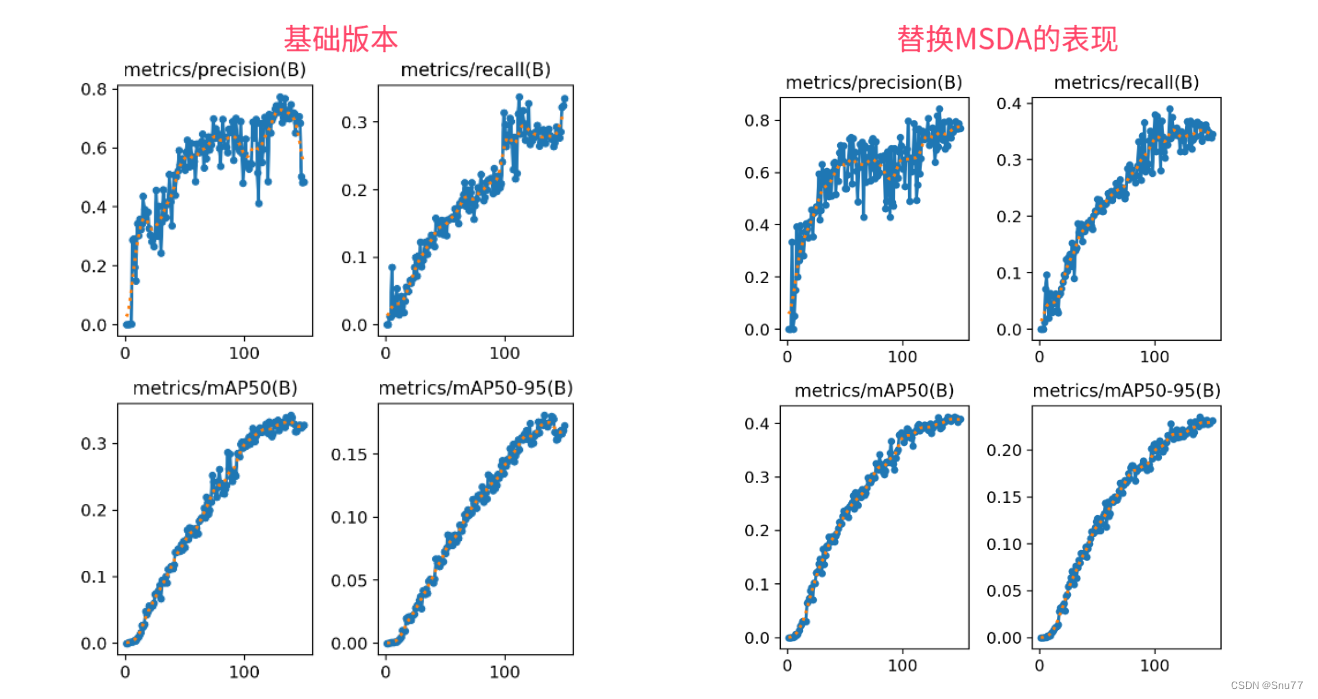
二、MSDA框架原理

论文地址:官方论文地址点击即可跳转
代码地址:官方代码地址点击即可跳转

在DilateFormer论文中,多尺度扩张注意力(MSDA)模块是为了利用自注意机制在不同尺度上的稀疏性。MSDA通过线性投影得到特征图X的相应查询、键和值。然后,将特征图的通道分成n个不同的头部,并在不同的头部中以不同的扩张率执行多尺度SWDA。具体来说,MSDA被公式化如下:对于每个头部i,进行SWDA操作,并且对所有的输出
MSDA(多尺度扩张注意力)模块的主要改进机制包括以下几点:
1. 多尺度特征提取:通过不同头部的自注意力机制,MSDA能够捕捉到多尺度的语义信息,这对于理解图像的不同抽象层次是非常重要的。
2. 稀疏性利用:MSDA利用了自注意力机制在不同尺度的稀疏性,降低了计算的冗余,同时保持了性能。
3. 头部通道分离:MSDA将特征图的通道分离成多个头部,每个头部处理不同的特征子集,这样可以并行处理,增强了模型的学习能力和效率。
4. 不同的扩张率:通过在不同头部设置不同的扩张率,MSDA能够在各个头部关注不同尺度的特征,从而能更加全面地捕捉图像中的信息。
5. 特征聚合:MSDA的输出通过连接操作合并,并通过线性层进行特征聚合,这样可以整合各个头部学习到的信息,得到更丰富的特征表示。
这些改进使得MSDA在不增加额外计算成本的情况下,提高了自注意力机制的效率和效果。

这幅图展示了ViT-Small的第三个多头自注意力(Multi-Head Self-Attention, MHSA)块的注意力图的可视化。在每张图中,一个特定的查询块(红色框内的区域)被用来展示其它各个块对它的注意力程度。注意力图显示了具有高注意力得分的块在查询块周围稀疏分布,而其它块的注意力得分较低。
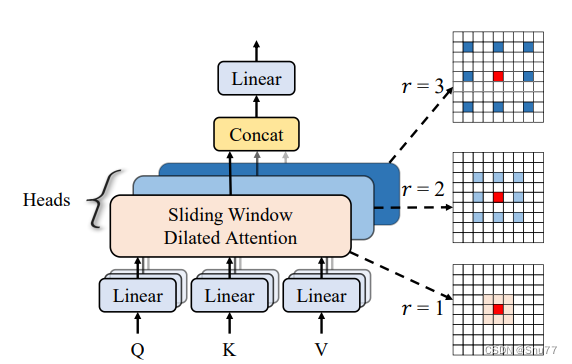
这张图展示了多尺度扩张注意力(MSDA)的工作原理。在MSDA中,特征图的通道首先被分割成不同的头部,然后每个头部内部使用不同的扩张率(dilation rates)r来执行自注意力操作。这些操作在围绕红色查询块的窗口内的彩色块之间进行。
图中的例子展示了三种不同的扩张率(r=1, 2, 3)(这里需要注意的是咱们我的网络中需要改成四种的扩张率),它们分别对应不同的感受野大小(3x3, 5x5, 7x7)。每个头部的自注意力操作针对的是其对应的扩张率和感受野。这样,模型能够在不同的尺度上捕捉图像特征,这些特征随后被连接在一起,并送入一个线性层进行特征聚合。
这种设计允许模型在不同的尺度上理解图像,从而提高对图像内容的整体理解。通过这种方法,MSDA不仅可以捕捉局部细节,也能够感知到更广泛区域的上下文信息,增强了模型的表现力。
三、MSDA核心代码
下面的代码是MSDA的核心代码,我们将其复制导'ultralytics/nn/modules'目录下,在其中创建一个文件,我这里起名为Dilation然后粘贴进去,其余使用方式看章节四。
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from functools import partial
from timm.models.layers import DropPath, to_2tuple, trunc_normal_
from timm.models.registry import register_model
from timm.models.vision_transformer import _cfg
class Mlp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class DilateAttention(nn.Module):
"Implementation of Dilate-attention"
def __init__(self, head_dim, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0, kernel_size=3, dilation=1):
super().__init__()
self.head_dim = head_dim
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
self.kernel_size=kernel_size
self.unfold = nn.Unfold(kernel_size, dilation, dilation*(kernel_size-1)//2, 1)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
def forward(self,q,k,v):
#B, C//3, H, W
B,d,H,W = q.shape
q = q.reshape([B, d//self.head_dim, self.head_dim, 1 ,H*W]).permute(0, 1, 4, 3, 2) # B,h,N,1,d
k = self.unfold(k).reshape([B, d//self.head_dim, self.head_dim, self.kernel_size*self.kernel_size, H*W]).permute(0, 1, 4, 2, 3) #B,h,N,d,k*k
attn = (q @ k) * self.scale # B,h,N,1,k*k
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
v = self.unfold(v).reshape([B, d//self.head_dim, self.head_dim, self.kernel_size*self.kernel_size, H*W]).permute(0, 1, 4, 3, 2) # B,h,N,k*k,d
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, H, W, d)
return x
class MultiDilatelocalAttention(nn.Module):
"Implementation of Dilate-attention"
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,
attn_drop=0.,proj_drop=0., kernel_size=3, dilation=[1, 2, 3, 4]):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.dilation = dilation
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
self.num_dilation = len(dilation)
assert num_heads % self.num_dilation == 0, f"num_heads{num_heads} must be the times of num_dilation{self.num_dilation}!!"
self.qkv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim * 3, 1, bias=qkv_bias)
self.dilate_attention = nn.ModuleList(
[DilateAttention(head_dim, qk_scale, attn_drop, kernel_size, dilation[i])
for i in range(self.num_dilation)])
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
# x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)# B, C, H, W
y = x.clone()
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, 3, self.num_dilation, C//self.num_dilation, H, W).permute(2, 1, 0, 3, 4, 5)
#num_dilation,3,B,C//num_dilation,H,W
y1 = y.reshape(B, self.num_dilation, C//self.num_dilation, H, W).permute(1, 0, 3, 4, 2 )
# num_dilation, B, H, W, C//num_dilation
for i in range(self.num_dilation):
y1[i] = self.dilate_attention[i](qkv[i][0], qkv[i][1], qkv[i][2])# B, H, W,C//num_dilation
y2 = y1.permute(1, 2, 3, 0, 4).reshape(B, H, W, C)
y3 = self.proj(y2)
y4 = self.proj_drop(y3).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return y4
class DilateBlock(nn.Module):
"Implementation of Dilate-attention block"
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=False,qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0.,act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, kernel_size=3, dilation=[1, 2, 3],
cpe_per_block=False):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.dilation = dilation
self.cpe_per_block = cpe_per_block
if self.cpe_per_block:
self.pos_embed = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1, groups=dim)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = MultiDilatelocalAttention(dim, num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
attn_drop=attn_drop, kernel_size=kernel_size, dilation=dilation)
self.drop_path = DropPath(
drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim,
act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(self, x):
if self.cpe_per_block:
x = x + self.pos_embed(x)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
#B, C, H, W
return x
class GlobalAttention(nn.Module):
"Implementation of self-attention"
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, qkv_bias=False,
qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim**-0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, H, W, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, H * W, 3, self.num_heads,
C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, H, W, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class GlobalBlock(nn.Module):
"""
Implementation of Transformer
"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=False,qk_scale=None, drop=0.,
attn_drop=0., drop_path=0., act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
cpe_per_block=False):
super().__init__()
self.cpe_per_block = cpe_per_block
if self.cpe_per_block:
self.pos_embed = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1, groups=dim)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = GlobalAttention(dim, num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(
drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim,
act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(self, x):
if self.cpe_per_block:
x = x + self.pos_embed(x)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return x
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
"""Image to Patch Embedding.
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, in_chans=3, hidden_dim=16,
patch_size=4, embed_dim=96, patch_way=None):
super().__init__()
img_size = to_2tuple(img_size)
patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)
patches_resolution = [img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1]]
self.num_patches = patches_resolution[0] * patches_resolution[1]
self.img_size = img_size
assert patch_way in ['overlaping', 'nonoverlaping', 'pointconv'],\
"the patch embedding way isn't exist!"
if patch_way == "nonoverlaping":
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
elif patch_way == "overlaping":
self.proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_chans, hidden_dim, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, bias=False), # 224x224
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
nn.GELU( ),
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, int(hidden_dim*2), kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, bias=False), # 112x112
nn.BatchNorm2d(int(hidden_dim*2)),
nn.GELU( ),
nn.Conv2d(int(hidden_dim*2), int(hidden_dim*4), kernel_size=3, stride=1,
padding=1, bias=False), # 112x112
nn.BatchNorm2d(int(hidden_dim*4)),
nn.GELU( ),
nn.Conv2d(int(hidden_dim*4), embed_dim, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, bias=False), # 56x56
)
else:
self.proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_chans, hidden_dim, kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, bias=False), # 112x112
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
nn.GELU( ),
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, int(hidden_dim*2), kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=False), # 112x112
nn.BatchNorm2d(int(hidden_dim*2)),
nn.GELU( ),
nn.Conv2d(int(hidden_dim*2), int(hidden_dim*4), kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, bias=False), # 56x56
nn.BatchNorm2d(int(hidden_dim*4)),
nn.GELU( ),
nn.Conv2d(int(hidden_dim*4), embed_dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=False), # 56x56
)
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
# FIXME look at relaxing size constraints
assert H == self.img_size[0] and W == self.img_size[1], \
f"Input image size ({H}*{W}) doesn't match model ({self.img_size[0]}*{self.img_size[1]})."
x = self.proj(x) # B, C, H, W
return x
class PatchMerging(nn.Module):
""" Patch Merging Layer.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, merging_way, cpe_per_satge, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d):
super().__init__()
assert merging_way in ['conv3_2', 'conv2_2', 'avgpool3_2', 'avgpool2_2'], \
"the merging way is not exist!"
self.cpe_per_satge = cpe_per_satge
if merging_way == 'conv3_2':
self.proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
norm_layer(out_channels),
)
elif merging_way == 'conv2_2':
self.proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0),
norm_layer(out_channels),
)
elif merging_way == 'avgpool3_2':
self.proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.AvgPool2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
norm_layer(out_channels),
)
else:
self.proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.AvgPool2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0),
norm_layer(out_channels),
)
if self.cpe_per_satge:
self.pos_embed = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=1, groups=out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
#x: B, C, H ,W
x = self.proj(x)
if self.cpe_per_satge:
x = x + self.pos_embed(x)
return x
class Dilatestage(nn.Module):
""" A basic Dilate Transformer layer for one stage.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, depth, num_heads, kernel_size, dilation,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0.,
attn_drop=0., drop_path=0., act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, cpe_per_satge=False, cpe_per_block=False,
downsample=True, merging_way=None):
super().__init__()
# build blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
DilateBlock(dim=dim, num_heads=num_heads,
kernel_size=kernel_size, dilation=dilation,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
qk_scale=qk_scale, drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer, cpe_per_block=cpe_per_block)
for i in range(depth)])
# patch merging layer
self.downsample = PatchMerging(dim, int(dim * 2), merging_way, cpe_per_satge) if downsample else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
for blk in self.blocks:
x = blk(x)
x = self.downsample(x)
return x
class Globalstage(nn.Module):
""" A basic Transformer layer for one stage."""
def __init__(self, dim, depth, num_heads, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,
drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0., act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
cpe_per_satge=False, cpe_per_block=False,
downsample=True, merging_way=None):
super().__init__()
# build blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
GlobalBlock(dim=dim, num_heads=num_heads,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
qk_scale=qk_scale, drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer, cpe_per_block=cpe_per_block)
for i in range(depth)])
# patch merging layer
self.downsample = PatchMerging(dim, int(dim*2), merging_way, cpe_per_satge) if downsample else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
for blk in self.blocks:
x = blk(x)
x = self.downsample(x)
return x
class Dilateformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000, embed_dim=96,
depths=[2, 2, 6, 2], num_heads=[3, 6, 12, 24], kernel_size=3, dilation=[1, 2, 3],
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.1,
norm_layer=partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6),
merging_way='conv3_2',
patch_way='overlaping',
dilate_attention=[True, True, False, False],
downsamples=[True, True, True, False],
cpe_per_satge=False, cpe_per_block=True):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_layers = len(depths)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_layers - 1))
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
norm_layer = norm_layer or partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6)
#patch embedding
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim, patch_way=patch_way)
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path, sum(depths))]
self.stages = nn.ModuleList()
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
if dilate_attention[i_layer]:
stage = Dilatestage(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
kernel_size=kernel_size,
dilation=dilation,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=downsamples[i_layer],
cpe_per_block=cpe_per_block,
cpe_per_satge=cpe_per_satge,
merging_way=merging_way
)
else:
stage = Globalstage(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=downsamples[i_layer],
cpe_per_block=cpe_per_block,
cpe_per_satge=cpe_per_satge,
merging_way=merging_way
)
self.stages.append(stage)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
@torch.jit.ignore
def no_weight_decay(self):
return {'absolute_pos_embed'}
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.patch_embed(x)
for stage in self.stages:
x = stage(x)
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.norm(x) # B L C
x = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # B C 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
return x
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x
@register_model
def dilateformer_tiny(pretrained=True, **kwargs):
model = Dilateformer(depths=[2, 2, 6, 2], embed_dim=72, num_heads=[ 3, 6, 12, 24 ], **kwargs)
model.default_cfg = _cfg()
return model
@register_model
def dilateformer_small(pretrained=True, **kwargs):
model = Dilateformer(depths=[3, 5, 8, 3], embed_dim=72, num_heads=[ 3, 6, 12, 24 ], **kwargs)
model.default_cfg = _cfg()
return model
@register_model
def dilateformer_base(pretrained=True, **kwargs):
model = Dilateformer(depths=[4, 8, 10, 3], embed_dim=96, num_heads=[ 3, 6, 12, 24 ], **kwargs)
model.default_cfg = _cfg()
return model
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.rand([1, 3, 224,224])
m = dilateformer_tiny(pretrained=False)
y = m(x)
print(y.shape)四、手把手教你添加MSDA模块
4.1 MSDA添加步骤
4.1.1 步骤一
首先我们找到如下的目录'ultralytics/nn/modules',然后在这个目录下创建一个py文件,名字为Dilation即可(你也可以根据你自己的习惯起),然后将MSDA的核心代码复制进去。
4.1.2 步骤二
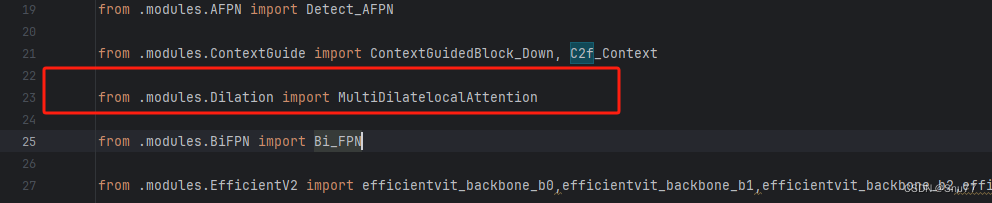
之后我们找到'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'文件,在其中注册我们的MSDA模块。
首先我们需要在文件的开头导入我们的MSDA模块,如下图所示->
4.1.3 步骤三
我们找到parse_model这个方法,可以用搜索也可以自己手动找,大概在六百多行吧。 我们找到如下的地方,然后将MSDA添加进去即可,模仿我添加即可,其中的两外两个模块,你没有删除即可。
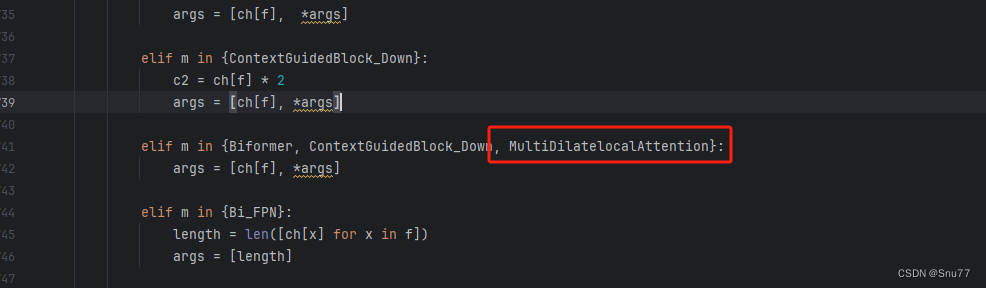
到此我们就注册成功了,可以修改yaml文件中输入MSDA使用这个模块了。
4.2 MSDA的yaml文件和训练截图
下面推荐几个版本的yaml文件给大家,大家可以复制进行训练,但是组合用很多具体那种最有效果都不一定,针对不同的数据集效果也不一样,我不可每一种都做实验,所以我下面推荐了几种我自己认为可能有效果的配合方式,你也可以自己进行组合。
4.2.1 MSDA的yaml版本一(推荐)
下面的添加MSDA是我实验结果的版本,我仅在大目标检测层的输出添加了一个MSDA模块,就涨点了0.05左右,所以大家可以在中等和小目标检测层都添加MSDA模块进行尝试,下面的yaml文件我会给大家推荐。
python
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [-1, 1, MultiDilatelocalAttention, []] # 22
- [[15, 18, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)4.2.2 MSDA的yaml版本二
添加的版本二具体那种适合你需要大家自己多做实验来尝试。
python
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, MultiDilatelocalAttention, []] # 16
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, MultiDilatelocalAttention, []] # 20
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 23 (P5/32-large)
- [-1, 1, MultiDilatelocalAttention, []] # 24
- [[16, 20, 24], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)4.3 推荐MSDA可添加的位置
MSDA是一种即插即用的可替换卷积的模块,其可以添加的位置有很多,添加的位置不同效果也不同,所以我下面推荐几个添加的位,置大家可以进行参考,当然不一定要按照我推荐的地方添加。
残差连接中:在残差网络的残差连接中加入MHSA**。**
Neck部分:YOLOv8的Neck部分负责特征融合,这里添加MSDA可以帮助模型更有效地融合不同层次的特征(yaml文件一和二)。
Backbone:可以替换中干网络中的卷积部分
能添加的位置很多,一篇文章很难全部介绍到,后期我会发文件里面集成上百种的改进机制,然后还有许多融合模块,给大家。
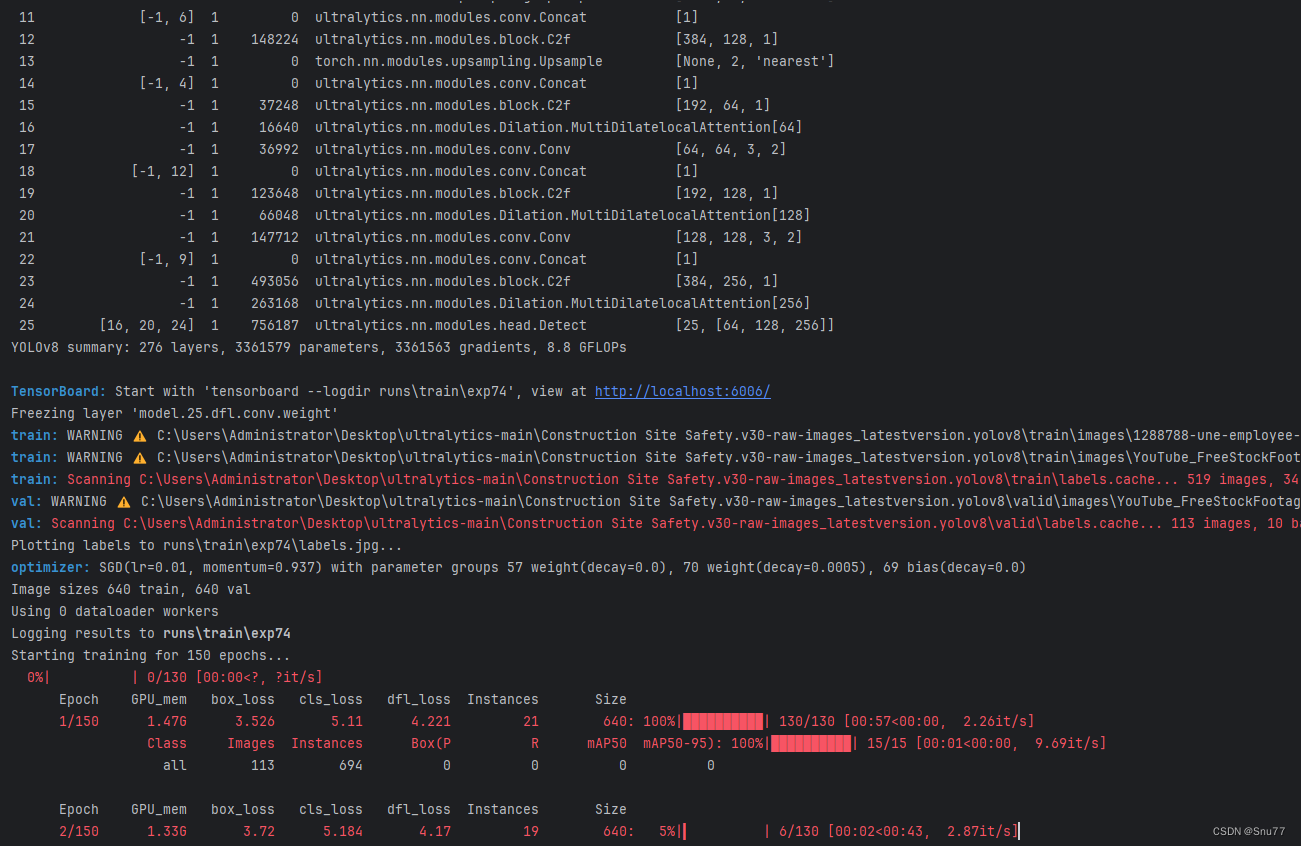
4.4 MSDA的训练过程截图
下面是添加了MSDA的训练截图。